Percent Difference Equations Formulas Calculator
Math - Science - Physics - Chemistry - Biology
Problem:
Solve for percent difference.
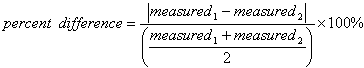
Enter Calculator Inputs:
Can you share this page? Because, it could help others.
Solution:
Change Equation or Formulas:
Tap or click to solve for a different unknown or equation
Percent Error Equation
| Solve for percent error |
Background
Calculating percent differences offers a clear metric for comparison and represents a fundamental tool in data analysis across various disciplines and practical applications. It lends itself to everything from academic research to everyday problem-solving.
The percent difference is a mathematical concept used to quantify the difference between two measurable values relative to their average. This calculation is widely used in various fields to compare two sets of data, demonstrating how significantly these data sets differ from one another on a normalized scale. The result is expressed as a percentage, providing a clear and intuitive measure of relative difference.
Equation
Percent difference is calculated using the formula:
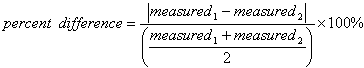
Where:
- Measured Value1 and Measured Value2 are the two numbers being compared.
- |Measured Value1 - Measured Value2| denotes the absolute difference between the two values.
How to Solve
To solve for the percent difference, follow these steps:
- Find the difference: Subtract one value from the other (order does not matter as you will take the absolute value).
- Calculate the average: Add the two values and divide by 2 to find the average.
- Divide the difference by the average: Take the absolute difference found in step 1 and divide it by the average calculated in step 2.
- Convert to percentage: Multiply the result in the step above by 100 to convert it into a percentage.
Example
Let's illustrate with an example:
Measured Value1 = 150, Measured Value2 = 130
Difference = |150 - 130| = 20
Average = (150 + 130) / 2 = 140
Divide = 20 / 140 = 0.142857
Percentage = 0.142857 × 100 = 14.29%
Thus, the percent difference between 150 and 130 is approximately 14.29%.
Fields/Degrees It Is Used In
- Statistics: Used to compare variations in data sets.
- Economics: Assess differences in economic indicators over time or between countries.
- Medicine: Compare the effectiveness of different treatments.
- Engineering: Evaluate discrepancies in measurements from expected values.
- Environmental Science: Measure changes in pollution levels or other environmental factors.
Real-Life Applications
- Market Analysis: Comparing product price differences over different regions.
- Quality Control: Determining inconsistencies in product batches.
- Academic Research: Analyzing differences in experimental results.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Tracking progress in patient recovery rates.
- Political Polling: Examining variations in polling data between different demographics.
Common Mistakes
- Forgetting Absolute Value: Neglecting to take the absolute value can result in incorrect negative percentages.
- Incorrect Average Calculation: Using the incorrect formula for calculating average—must be the simple mean.
- Rounding Errors: Early rounding can lead to less accurate percent differences.
- Mixing Percentage Points and Percent: Confusing a change in percentage points for a percent difference.
- Ignoring Sample Size: Failing to account for the size of the compared datasets can mislead conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can the percent difference be negative?
No, the percent difference is always non-negative because it is defined using the absolute difference between the values. - What is the difference between percent difference and percent change?
Percent change relates the difference to the original value, typically used when comparing an old value to a new one. Percent difference compares two values symmetrically without primary reference. - Is it applicable to zero values?
Percent difference can become infinitely large or undefined if one of the values is zero, as the average in the denominator approaches zero. - How does sample size affect the percent difference?
Larger sample sizes can give more reliable percent differences as they reduce the impact of outliers and random variability. - Can percent difference be used for more than two values?
Typically, the percent difference is defined for two values. For more values, consider using variance or standard deviation to measure spread.
Online Web Apps, Rich Internet Application, Technical Tools, Specifications, How to Guides, Training, Applications, Examples, Tutorials, Reviews, Answers, Test Review Resources, Analysis, Homework Solutions, Worksheets, Help, Data and Information for Engineers, Technicians, Teachers, Tutors, Researchers, K-12 Education, College and High School Students, Science Fair Projects and Scientists
By Jimmy Raymond
![]()
Contact: aj@ajdesigner.com
Privacy Policy, Disclaimer and Terms
Copyright 2002-2015