Chezy Equations Formulas Calculator
Fluid Mechanics Open Channel Flow
Problem:
Solve for flow velocity.
Enter Calculator Inputs:
Can you share this page? Because, it could help others.
Solution:
Solution In Other Units:
Input Unit Conversions:
Change Equation or Formulas:
Tap or click to solve for a different unknown or equation
| flow velocity | |
| Chezy coefficient | |
| hydraulic radius | |
| slope |
Chezy Coefficient
| Chezy coefficient | |
| roughness coefficient | |
| hydraulic radius |
References - Books:
Lindeburg, Michael R. 1992. Engineer In Training Reference Manual. Professional Publication, Inc. 8th Edition.
Background
Calculating water flow velocity in channels is crucial for designing and managing hydraulic structures. The Chezy formula is a widely used empirical equation for estimating the velocity of water flowing through a channel with a certain roughness and slope. It is named after the French engineer Antoine Chézy, who introduced it in the 18th century.
Equation
The equation for flow velocity (v) according to the Chezy formula is:
where:
- v is the flow velocity (m/s)
- C is the Chezy coefficient, which is a function of the channel roughness and dimensions (m1/2/s)
- rh is the hydraulic radius, which is the area of the flow (A) divided by the wetted perimeter (P) (m)
- S is the slope of the energy line or hydraulic grade line, often approximated by the slope of the channel bed (dimensionless)
How to Solve
To solve for flow velocity using the Chezy formula, follow these steps:
- Determine the Hydraulic Radius (rh): Measure or calculate the cross-sectional area (A) of flow and the wetted perimeter (P) of the channel. The hydraulic radius is then ( rh = A/P ).
- Find the Chezy Coefficient (C): The Chezy coefficient can be determined through experimental data, tables, or formulas such as the Bazin or Manning equations, which consider the channel's roughness and other characteristics.
- Calculate the Slope (S): The slope of the energy line is often approximated by the slope of the channel bed itself. This can be obtained by taking the vertical drop per unit length of the channel.
- Apply the Chezy formula: With values for rh, C, and S, use the Chezy equation to solve for the flow velocity v.
Example
Suppose we have a rectangular channel with a width of 3 meters and a water depth of 2 meters. The channel has a bed slope of 0.001 and a Chezy coefficient of 60 m1/2/s.
Hydraulic Radius (rh):
rh = A / P = (width x depth) / (width + 2 x depth) = (3 x 2) / (3 + 2 x 2) = 6 / 7 = 0.857 m
Apply the Chezy formula:
![]()
The water flow velocity through the channel is approximately 1.75 m/s.
Fields/Degrees It Is Used In
- Civil Engineering
- Environmental Engineering
- Hydraulic Engineering
- Water Resources Engineering
- Agricultural Engineering
Real-life Applications
- Designing irrigation canals to ensure efficient water delivery to agricultural fields.
- Calculating the flow in sewer systems for proper waste management.
- Determining river velocities for navigational purposes and flood risk assessment.
- Sizing stormwater drainage channels to prevent urban flooding.
- Assessing the hydraulic performance of natural streams and channels for habitat conservation.
Common Mistakes
- Confusing the slope of the channel bed with the hydraulic gradient.
- Using an incorrect value for the Chezy coefficient by not correctly accounting for the surface roughness.
- Incorrect calculation of the hydraulic radius, mainly when the channel shape is irregular.
- Inaccurate measurements of channel dimensions lead to errors in estimating the flow area and wetted perimeter.
- Failing to recognize that the Chezy coefficient can change due to factors such as vegetation growth, sediment deposition, or channel wear.
Frequently Asked Questions with Answers
- What factors affect the Chezy coefficient?
The Chezy coefficient is influenced by the roughness of the channel surface, channel shape, and sediment size within the flow. - Is the Chezy formula valid for all types of flow?
The Chezy formula is primarily used for uniform flow conditions, and it may need to be revised for rapidly varying flows or for flows that still need to be fully developed. - Can the Chezy coefficient be used for both natural and artificial channels?
Yes, the Chezy coefficient can be applied to natural streams and man-made channels, with appropriate adjustments for each's roughness characteristics. - What is the relationship between the Chezy coefficient and the Manning coefficient?
The Chezy coefficient is associated to the Manning coefficient through the equation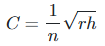
where n is the Manning coefficient. - How is the slope of the channel measured?
The slope is typically measured as the change in elevation over a certain length of the channel. It may be measured through land surveys or topographical maps.
Online Web Apps, Rich Internet Application, Technical Tools, Specifications, How to Guides, Training, Applications, Examples, Tutorials, Reviews, Answers, Test Review Resources, Analysis, Homework Solutions, Worksheets, Help, Data and Information for Engineers, Technicians, Teachers, Tutors, Researchers, K-12 Education, College and High School Students, Science Fair Projects and Scientists
By Jimmy Raymond
![]()
Contact: aj@ajdesigner.com
Privacy Policy, Disclaimer and Terms
Copyright 2002-2015