Parallel Plate Capacitor Design Equations Formulas Calculator
Science - Physics - Electricity - Capacitance
Problem:
Solve for capacitance.
Note: free space permittivity = ε0 = 8.85 F/m
Enter Calculator Inputs:
Can you share this page? Because, it could help others.
Solution:
Solution In Other Units:
Input Unit Conversions:
Change Equation or Formulas:
Tap or click to solve for a different unknown or equation
| capacitance | |
| permittivity | |
| area | |
| separation distance |
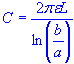 | capacitance |
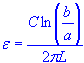 | permittivity |
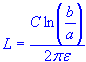 | length of conductors |
| outer conductor diameter | |
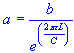 | inner conductor diameter |
| capacitance | |
| electrical charge | |
| potential difference |
| stored energy | |
| capacitance | |
| potential difference |
| stored energy | |
| capacitance | |
| electrical charge |
| energy storage | |
| electrical charge | |
| potential difference |
References - Books:
Tipler, Paul A. 1995. Physics For Scientists and Engineers. Worth Publishers. 3rd ed.
Background
Capacitance measures a capacitor's ability to store electric charge. A parallel plate capacitor, one of the most straightforward capacitor configurations, consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material or dielectric. The parallel plate capacitor capacitance depends on three factors:
- The area (A) of the plates
- The separation distance (s) between the plates
- The permittivity (ε) of the dielectric material between the plates
Equation
The capacitance (C) is calculated using the formula:
C = εA / s
Where:
- C is the capacitance in farads (F).
- ε is the dielectric material permittivity (in farads per meter, F/m).
- A is the area of one of the plates (in square meters, m²).
- s is the separation distance of the plates (in meters, m).
How to Solve
To solve for the capacitance, follow these steps:
- Identify the permittivity of the dielectric material. This may be given, or it may need to be calculated by multiplying the relative permittivity (εᵣ) by the permittivity of free space (ε₀).
- Measure the area of one of the conductive plates.
- Determine the distance between the plates.
- Plug the values into the formula.
- Calculate the result, which will give you the capacitance in farads.
Example
Suppose you have a parallel plate capacitor with a plate area of (0.01 m²), a plate separation of (0.001 m), and the dielectric is air with a relative permittivity (εᵣ) of approximately 1. The free space (ε₀) permittivity is ( 8.854 x 10-12 F/m ).
First, calculate the permittivity (ε), which is:
ε = εᵣ * ε₀ = 1 * 8.854 x 10-12 F/m
Now plug the values into the formula for capacitance:
C = εA / s = 8.854 x 10-12 F/m * 0.01 m / 0.001 m
C = 8.854 x 10-11 F
C = 88.54 pF (picoFarads)
Fields/Degrees Used In
- Electrical Engineering: In the design and analysis of electronic circuits.
- Physics: Understanding energy storage and electrical fields in academic research and education.
- Information Technology: For memory storage devices like dynamic random-access memory (DRAM).
- Telecommunications: In the tuning circuits of radio and TV receivers.
- Mechanical Engineering: In sensing applications, such as pressure sensors or energy storage in power grids.
Real-life Applications
- Filtering unwanted noise in electronic circuits.
- Controlling the timing in oscillators and signal processors.
- Power supply units use capacitors to store and release energy as needed.
- Touch screens employ capacitors to detect the position of touches.
- Flash units in cameras use a capacitor to quickly release a large amount of energy to produce a flash.
Common Mistakes
- Confusing permittivity of the material with the relative permittivity.
- Mixing up the units of area, often by failing to convert to square meters from centimeters or millimeters.
- Not accounting for the plate separation correctly, such as using the thickness of a plate instead of the space between them.
- Neglecting the edge effects on plates that have a large aspect ratio.
- Assuming the permittivity remains constant, it can depend on factors like frequency or temperature.
Frequently Asked Questions with Answers
- What is permittivity?
Permittivity measures how easily electric fields can permeate a material. It's a property of the dielectric material between the plates of a capacitor. - What units are used for capacitance?
Capacitance is measured in farads (F), a derived unit of electric capacitance in the International System of Units (SI). - Can the plate area or separation affect the overall capacitance value?
Yes, the plate area and the separation distance affect capacitance. Increasing the plate area increases capacitance while increasing the separation distance decreases capacitance. - What happens to the capacitance if a different dielectric is used?
Changing the dielectric material changes its permittivity. A higher permittivity increases capacitance, while a lower permittivity decreases it. - Are there limitations to the parallel plate capacitor formula?
Yes, the formula assumes an ideal parallel plate capacitor with uniform electric fields between the plates, which is not always the case in practical applications. Edge effects and other non-ideal conditions can cause deviations from the theoretical capacitance calculated.
Online Web Apps, Rich Internet Application, Technical Tools, Specifications, How to Guides, Training, Applications, Examples, Tutorials, Reviews, Answers, Test Review Resources, Analysis, Homework Solutions, Worksheets, Help, Data and Information for Engineers, Technicians, Teachers, Tutors, Researchers, K-12 Education, College and High School Students, Science Fair Projects and Scientists
By Jimmy Raymond
![]()
Contact: aj@ajdesigner.com
Privacy Policy, Disclaimer and Terms
Copyright 2002-2015